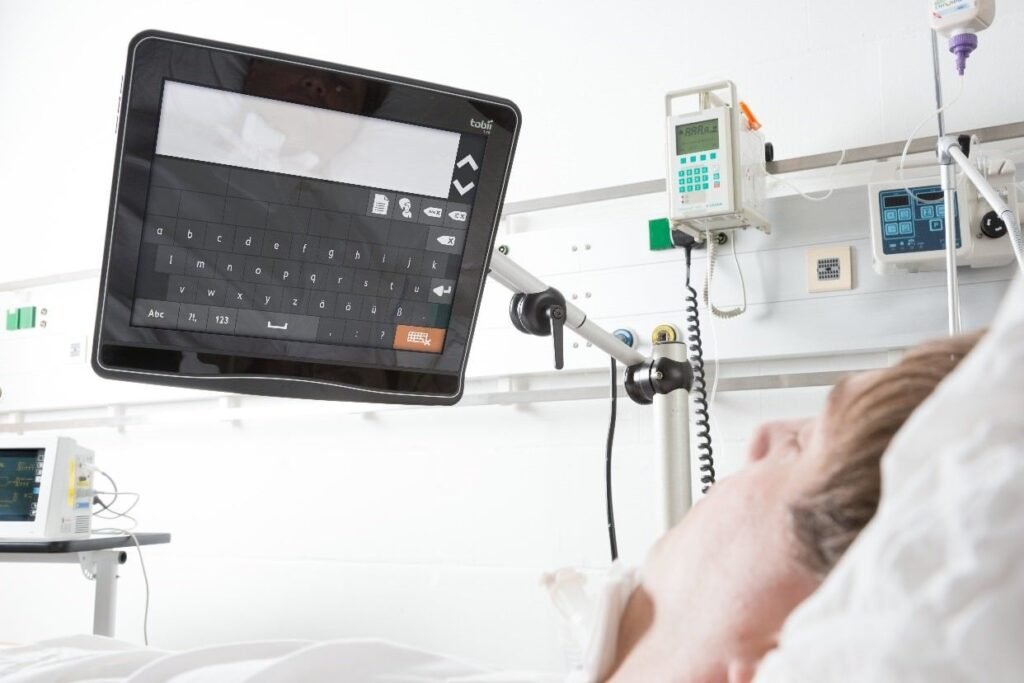
Hospital environment and possible difficulties
Staying in a hospital environment, especially in an intensive care unit, is often stressful for patients. Patients can be confused, scared and tense, and what is normally taken for granted in everyday life, including communication, can now become an insurmountable obstacle. Illness, medications, pain, weakness, procedures they underwent, all of this can prevent patients from normal communication, and that at the very moment when it can be of vital importance.
On the other hand, patient care staff have to deal with stress and a fast pace of work, a busy environment and extremely demanding work, while trying to judge as best as possible, reading subtle signs, following their experience or feeling, the condition and the needs of those who often care for them. I can't say that myself.
The role of assisted communication tools is to rebuild the bridge of communication between those in need and those who can best help them. They significantly improve the quality of life and work in the hospital and contribute to faster and easier overcoming of difficulties, and ultimately to recovery.

Who are these products intended for?
These assisted communication devices are intended for patients with different diagnoses and different severity of communication difficulties. Their role can be divided into three basic functions:
- facilitating communication between hospital staff and patients who have communication difficulties or are completely prevented from communicating,
- greater independence of patients (independent control of lights, television, hospital bed, calling a nurse),
- independent access to the computer, the Internet, social media and telecommunications services.
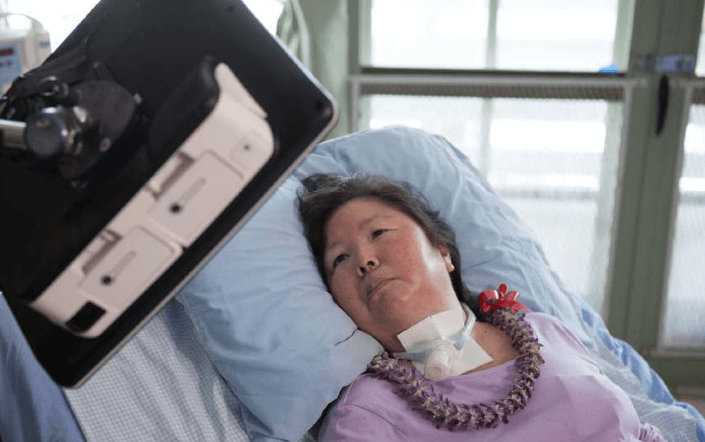
Benefits for patients
Better communication enables patients to receive better care and improve their emotional state. They can express their wishes and needs, emotions, intensity and location of pain and much more to hospital staff and families. Additional benefits, whether it's a short-term or long-term hospital stay:
- greater independence in managing devices in your environment,
- independent access to computers, telecommunications, social networks, etc.
- the possibility of participating in education, work and many daily activities that can be done via computer,
- early assessment of possible future needs for assistive technology.
Benefits for staff
By building better communication with patients, the staff can help them better, but also make their stay in the hospital easier emotionally. A stronger bond and trust is created between patients and healthcare staff, which is of immense importance in the recovery process. Assistive technology devices bring many benefits, and only some of them are:
- preventing misunderstandings and even mistakes due to misinterpreted messages or patients' inability to express themselves verbally and non-verbally,
- better collection of information about the patient, about his condition and needs, and thus better quality and properly directed care
- less need for staff in everyday situations that do not require professional help, such as turning on the lights, turning off the TV, etc.

Benefits for healthcare institutions
By introducing communication tools, healthcare institutions can expect improved treatment outcomes and greater patient satisfaction, as well as greater productivity and staff satisfaction. Assistive technology provides a more comfortable environment and makes it easier for professional staff to understand patient needs and provide care. Healthcare institutions will also have other benefits:
- a lower number of medical errors or patients returning to the hospital due to difficult or impossible communication
- fewer accidents due to greater independence of patients in managing devices in their environment
- greater efficiency and better service of health personnel
- reducing the possibility of late diagnosis and care, and thus shortening the hospital stay
It is clear that improving the quality of services and patient satisfaction, as well as increasing the efficiency and satisfaction of staff ultimately results in cost reduction. Thus, even a small device from a hospital room or bedside in an intensive care unit can manage the rationality and efficiency of a large hospital system.